Heat of reaction for, CO(g) + 1/2 O2(g)→ CO2(g)at constant V is 67.71 K cal at 17^° C. The heat of reaction at constant P at 17^° C is
Par un écrivain mystérieux
Description
Heat of reaction for, CO(g) + 1/2 O2(g)→ CO2(g)at constant V is 67.71 K cal at 17^° C. The heat of reaction at constant P at 17^° C is
Heat of reaction for- CO-g- - 1-2 O2-g- CO2-g-at constant V is-67-71 K cal at 17- C- The heat of reaction at constant P at 17- C is
Heat of reaction for- CO-g- - 1-2 O2-g- CO2-g-at constant V is-67-71 K cal at 17- C- The heat of reaction at constant P at 17- C is

Activation of C−H Bonds by Metal Complexes

Heat of reaction for, CO(g) + 1/2 O2(g)→ CO2(g)at constant V is 67.71 K cal at 17^° C. The heat of reaction at constant P at 17^° C is
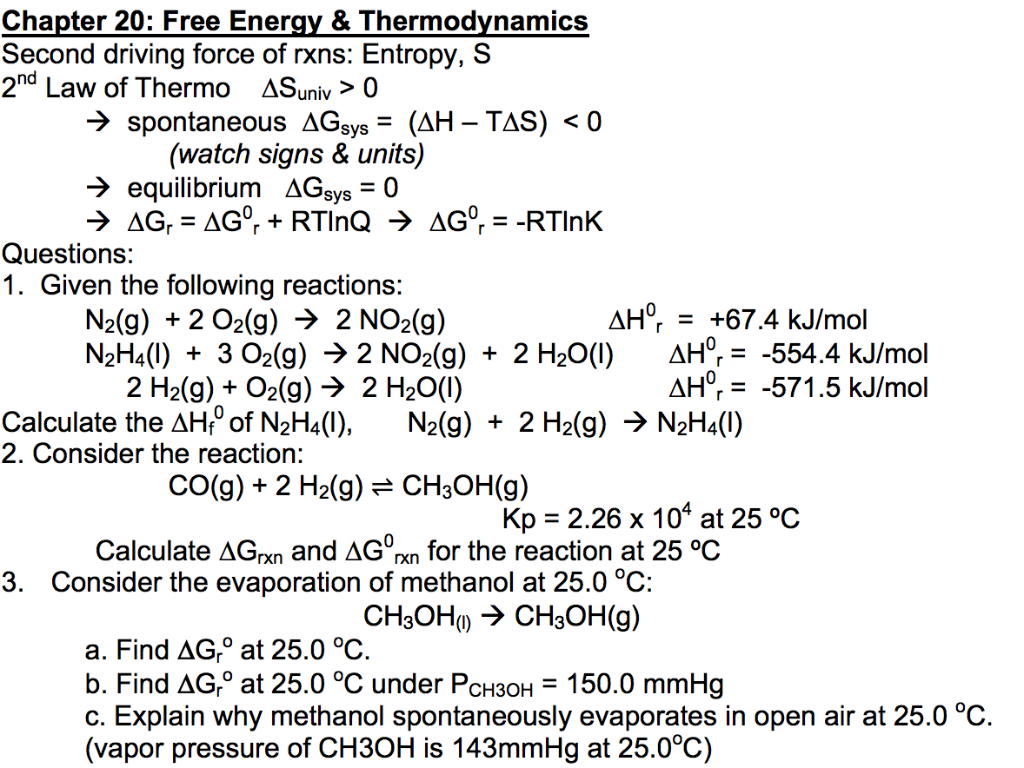
Solved 1. Given the following reactions: N2(g) + 2 O2(g) à 2
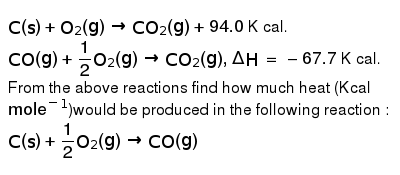
C(s)+O(2)(g)rarr CO(2)(g)+94.0 K cal. CO(g)+(1)/(2)O(2)(g)rarr CO(2)

A 2.200-g sample of quino ne $$ (C_6H_4O_2) $$ is burned

Solved Calculate the standard Gibbs free energy of rection

5.4.6 Hess's Law of Heat Summation [1840] - ppt download

2. Heat of reaction , COCO) + 0.1) - COX) constant V is -67.71 Kcal 17°C. The heat of reaction constant Pat 17°C is :- (1)-68.0 Kcal (2) + 68.0 Kcal (3) - 67.42 Kcal (4) None The reaction

Heat of reaction C_6H_{12}O_6(s) + 6O_2 (g) rightarrow 6CO_2(g) +6H_2O(v) constant pressure is -651 kcal 17°C. Calculate the heat of reaction constant volume 17°C.

Solved For the reaction 2CO(g) => C(s) + CO2(g), Keq = 7.7 x

Ch6.1 The Nature of Energy Energy – the capacity to do work or to produce heat. Law of Conservation of Energy – energy can be converted from one form to. - ppt download

Bioprocess Engineering Principles 2nd Edition Solutions Manual [2nd Edition, 2nd ed.] 9780122208515

Heat of reaction for; CO(g) + 1/2O2(g)→CO2(g) at constant V is - 67.71 cal 17^oC . The heat of reaction at constant P at 17^oC
depuis
par adulte (le prix varie selon la taille du groupe)